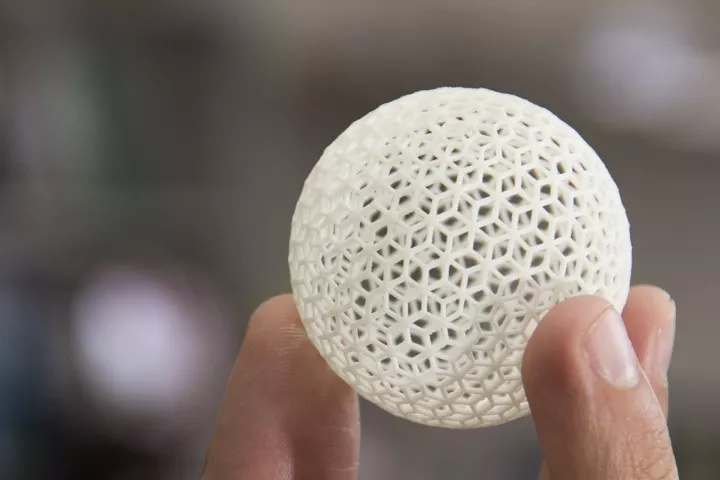
Microscope
A Brief Guide – Maintenance and Care of the Microscope
Microscopes with digital cameras may find the images produced degrading in image quality. A Brief Guide – Maintenance and Care of the Microscope.

As the years have gone by, several procedures have been recommended to maintain microscope quality but many users still are not sure what is the best way to go about it. A better cleaning method changes depending on the optical surface, as well as the substance that needs to be removed as studies on a microscope in Singapore, have shown.
If a microscope remains unused over a long period the quality of images produced by it will reduce as will the quality of a microscope that is used regularly since contaminants build up and may not fully clear up when cleaned.
Some of the dirt may sometimes come from the environment, like dust, but other times contaminants are introduced by the people who use the microscope in areas in contact with the body such as eyelashes, hands, and areas where moisture is captured by breathing on it over time. Problem areas include:
- Both sides of the coverslip
- The outside of the front lens of the objective
- The microscope slide
- Glass surfaces that come into contact with the hands in the path or the light
- The upper lens of the condenser
- Both surfaces of the eyepiece
- The reticule’s upper surface
- The outer glass coverings where light exits
- The protective cover and surface of the camera sensor
The front lens of the objective is more sensitive to light than other optical surfaces as are the optical elements near or at the conjugate field. Objects seem to appear in sharp focus when imposed on the specimen image. The higher quality of the optical components, the more blemishes are likely to interfere with the findings.

For all the dry objectives, a greater danger of soiling the lens at the front is presented when the free working distance and surface area of the concave front lens happen to be smaller. The immersion objectives front lens needs to be cleaned and its residue removed before applying fresh immersion fluid to prevent blurred images from new and old intermission fluid mixing.
Even though the fluid’s use is necessary for peak performance, improper use or failure to remove it immediately after each use can lead to serious contamination of the specimen and may cause damage to the microscope and improper findings.
Microscopes with digital cameras may find the images produced degrading in image quality because of contamination on filter elements used in the adapter of the camera and on the optical glass window put in to seal the housing of the camera and protect the charge-coupled device or the complementary metal oxide semiconductor.
If dark specs can be seen in digital images that are not on the specimen plane, the most likely cause is contamination on the image sensor or any other filter service as shown in the microscope in Singapore and other product studies carried out. The manufacturer’s recommendations about cleaning the microscopes should be taken into consideration while cleaning them and the cameras whenever dirt is on them.
Helpful Resources:
1. 16 Best (free) AMP – (Accelerated Mobile Pages) WordPress Plugins
2. 16 Best Free SEO WordPress plugins for your Blogs & websites
3. Riverdale Cast List For The TV Show Riverdale
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
How AI and Machine Learning are Revolutionizing Healthcare Industry?
Among all the industries set to be impacted by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), the healthcare sector stands to benefit the most.

Among all the industries set to be impacted by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), the healthcare sector stands to benefit the most.
In fact, in a report made by a consulting firm, Frost & Sullivan, it was stated that the healthcare AI market is estimated to experience a compound annual growth rate of 40% through 2021.
It is mainly because technologies like Data Science, Machine Learning, and AI are capable of improving healthcare outcomes by 30 to 40% while simultaneously reducing the costs of treatment in half.
As per Accenture’s reports, AI applications can create yearly savings of $150 billion by 2026 for US healthcare.
These innovative technologies are typically used in healthcare to handle the complexity and growth of medical data. These AI solutions are used in healthcare to handle the complexity and growth of medical data. The benefits offered by AI and machine learning include automated disease diagnosis, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, personalization of treatment pathways, helping patients in real-time, advancement in treatments, and cutting costs. And these are only a few.
Let’s take a look at how AI and machine learning impact the healthcare industry.
Table of Contents
1. Improved Automated Disease Diagnosis
The medical industry is already using AI to improve medical diagnosis. For instance, the Beijing-based artificial intelligence high-tech company is using AI-aided medical image diagnosis to improve reading CT scans and x-rays. Read more about Beijing-based Inversion here.
Stanford University researchers have created an AI algorithm that can spot and diagnose skin cancer. Also, Google has created an AI program to detect metastasis using high-level image recognition. The company claims 99% accuracy in metastatic breast cancer detection.
Moreover, since AI can analyze large volumes of data, it can detect disease and helps with clinical decisions.
2. Maintaining Wellness
Using AI in consumer health applications is helping people stay healthy. People don’t need a doctor as often as they used to before. Some apps encourage healthier behavior in individuals and assist in proactively managing a healthy lifestyle.
For instance, apps like MyFitnessPal can help you to track your diet programs through a database that offers nutrition information for more than 5 million foods.
Furthermore, AI helps healthcare professionals to understand the everyday patterns and needs of patients better. They are also able to provide better feedback, direction, and support for staying healthy.
3. Personalizing Treatment
Not all patients respond to drugs and treatment schedules in the same manner, so personalized treatment is very beneficial. However, it is difficult to identify which factors should affect the choice of treatment. This is where machine learning comes in.
Machine Learning can simplify complicated statistical work. It can help determine which characteristics indicate that a patient or a group of patients will have an appropriate response to a specific treatment.
Machine learning does this by cross-referencing similar patients and comparing their treatments and outcomes, making it much easier for doctors to design the right treatment plan.
Also, as per a new study by the Cleveland Clinic, artificial intelligence and machine learning networks can personalize radiation therapy for lung cancer. AI can learn from imaging and electronic health records. It can predict if an individual patient could fail radiation treatments, thus individualizing radiotherapy treatments for patients with lung cancers.
Yet in another study made by the Institute of Cancer Research, scientists with the help of artificial intelligence have spotted patterns in breast cancer and exposed five new types of the disease each matched to different personalized treatments.
4. Helping Patients in Real-Time
Innovative and advanced healthcare Bots today can learn and mimic human conversations, detect emotions that allow empathetic engagement with patients, incorporate Natural Language Processing, sentiment analysis, and concept mining into chat scripts, and recognize the intricate image to analyze photos, handwritten notes, and barcodes. It is not only about sending messages.
However, the primary reason why healthcare bots exist is to help patients quickly and in real-time simply by sending a message, making it great for emergencies.
It can even assist patients in managing medications by offering information on types of medications and recommended doses.
For instance, the Microsoft Healthcare Bot service helps healthcare organizations to build and set up an AI-powered, compliant, conversational healthcare experience.
It is suitable for healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, telemedicine providers, and health insurers. The Health Bot Service contains built-in scenarios including a symptom checker; general information about conditions, symptoms, causes, complications, and more; finding doctor type; health plan inquiries; finding providers, and scheduling appointments.
5. Advancement in Treatments
With the help of AI, new treatment methods are being generated and introduced, including robotic surgery. In 2018, over 5,000 surgical robots were used in over 1 million procedures across the world. And the procedures encompassed orthopedics, urology, gynecology, neurology, otolaryngology, rectal and colon, dental implants, hair transplants, and more.
AI is also used for diabetes management. And a Boston-based Bionic Pancreas that uses machine learning has been introduced to aid adults and children with type 1 diabetes. Read more about the device here.
Furthermore, wound healing by printing skin cells, 3D printing of human body parts, and blood vessel reproduction are all made possible through AI.
6. Reduce Costs
Health Policy Brief noticed that in 2012, $300 billion was being spent on pointless healthcare costs. The costs were associated with fraud, waste, and abuse; absence of or low value-added work; and no collaboration between stakeholders.
As per Frost & Sullivan reports, AI can improve outcomes by 30- 40% and reduce the cost of treatment by as much as 50%. When there is an improvement in precision and efficiency, there will be fewer human errors. There will be a decrease in doctor visits. Moreover, doctors can obtain information from data for patients who are at risk of certain diseases to avert hospital readmissions.
If you look at the bigger scenario, as per Healthcare IT news, potential cost savings in AI applications in billions of dollars are shown below:
Machine learning and AI have the potential to drastically change the cost and quality curve in healthcare.
7. Winding Up
AI is the game-changer in the healthcare industry. It has changed the role of doctors and even the role of patients. It has transformed how diseases are detected and diagnosed, how treatments are offered, helped discover new treatment methods, and saves time and cost as well.
No doubt, challenges are being faced by AI and machine learning in the healthcare industry, but it is ever-growing and expanding. It has become an inherent part of medical care in many parts of the world.
Helpful Resources:
1. 16 Best (free) AMP – (Accelerated Mobile Pages) WordPress Plugins
2. Top 10 Artificial Intelligence (AI) App Development Trends
3. Artificial Intelligence And Its Demands To The Programmers
4. Artificial intelligence (AI): Friend or Foe to Future Designers?
5. How Augmented Reality Will Change The Future Of the Design Industry

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years agoBuy IG likes and buy organic Instagram followers: where to buy them and how?

 Instagram3 years ago
Instagram3 years ago100% Genuine Instagram Followers & Likes with Guaranteed Tool

 Business5 years ago
Business5 years ago7 Must Have Digital Marketing Tools For Your Small Businesses

 Instagram4 years ago
Instagram4 years agoInstagram Followers And Likes – Online Social Media Platform